Exponential Functions Explained

Exponential functions are what happens when growth feeds on itself.
Linear growth adds the same amount each step. Exponential growth multiplies by the same factor. The difference seems subtle. It isn't. Exponential growth starts slow and ends overwhelming.
What You'll Learn
This series covers the mathematics of exponential functions:
- What Is an Exponential Function? — When the variable is the power
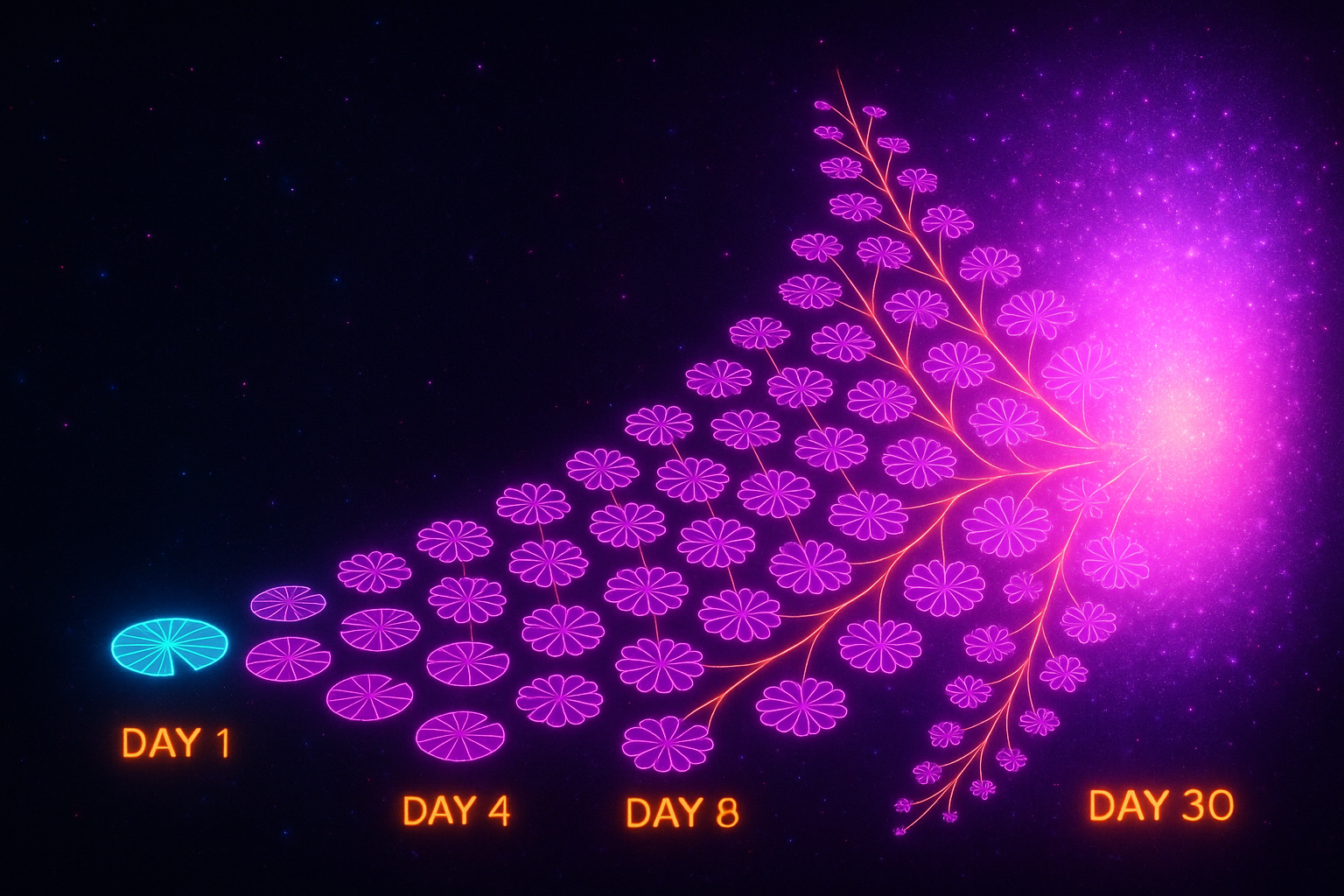
- Exponential Growth — Doubling, and doubling again, and doubling again
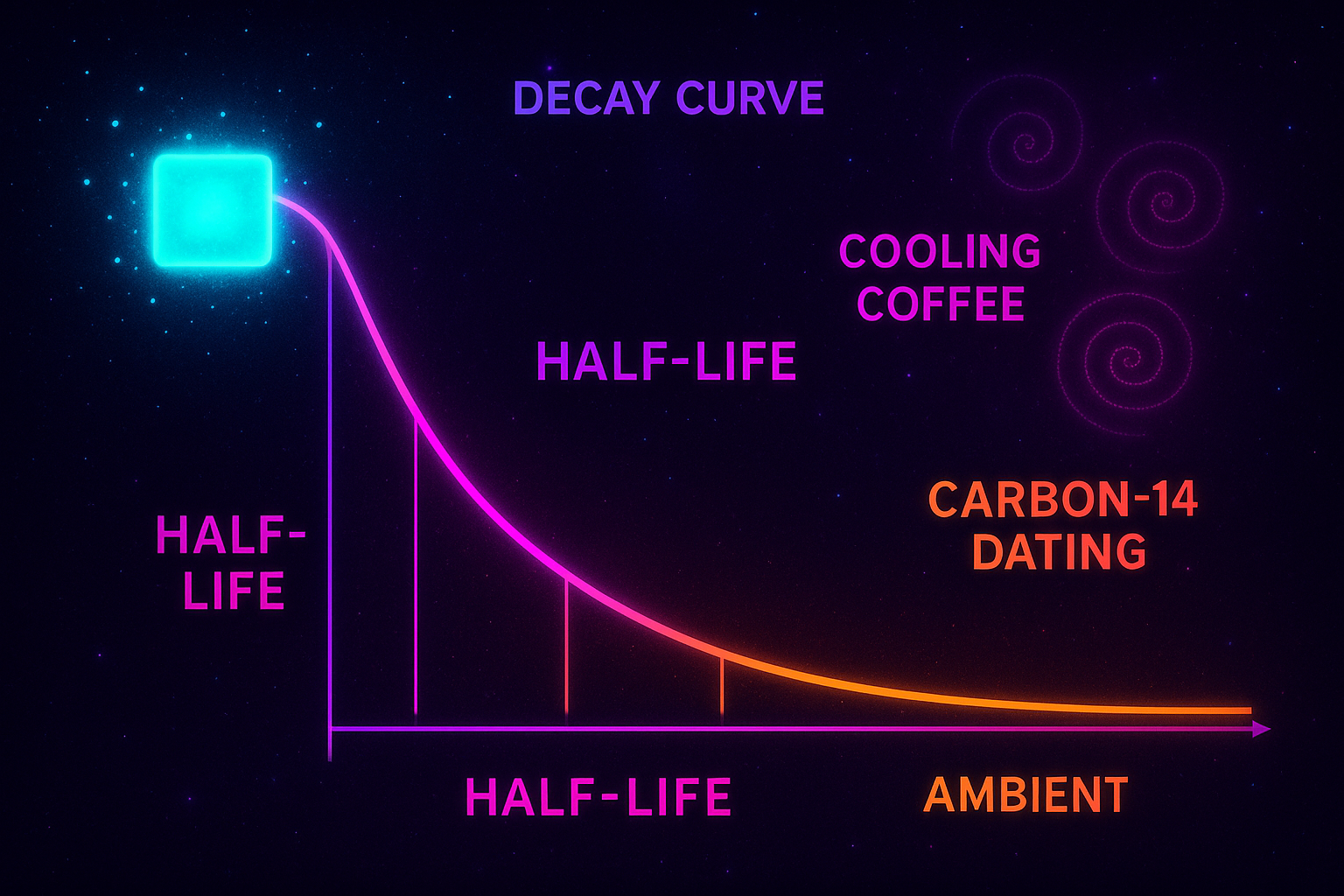
- Exponential Decay — Half-lives and the mathematics of shrinking
- The Number e — Why 2.71828... is the natural base for growth
- Compound Interest — Exponential growth in your bank account
- The Function eˣ — The most important function in mathematics
- Exponential vs. Polynomial — Why exponentials always win
- Synthesis — Exponentials as the language of multiplicative processes
Prerequisites
- Exponents and their rules
- Basic algebra (variables, equations, graphs)
- Familiarity with geometric sequences
Why This Matters
Exponential functions describe:
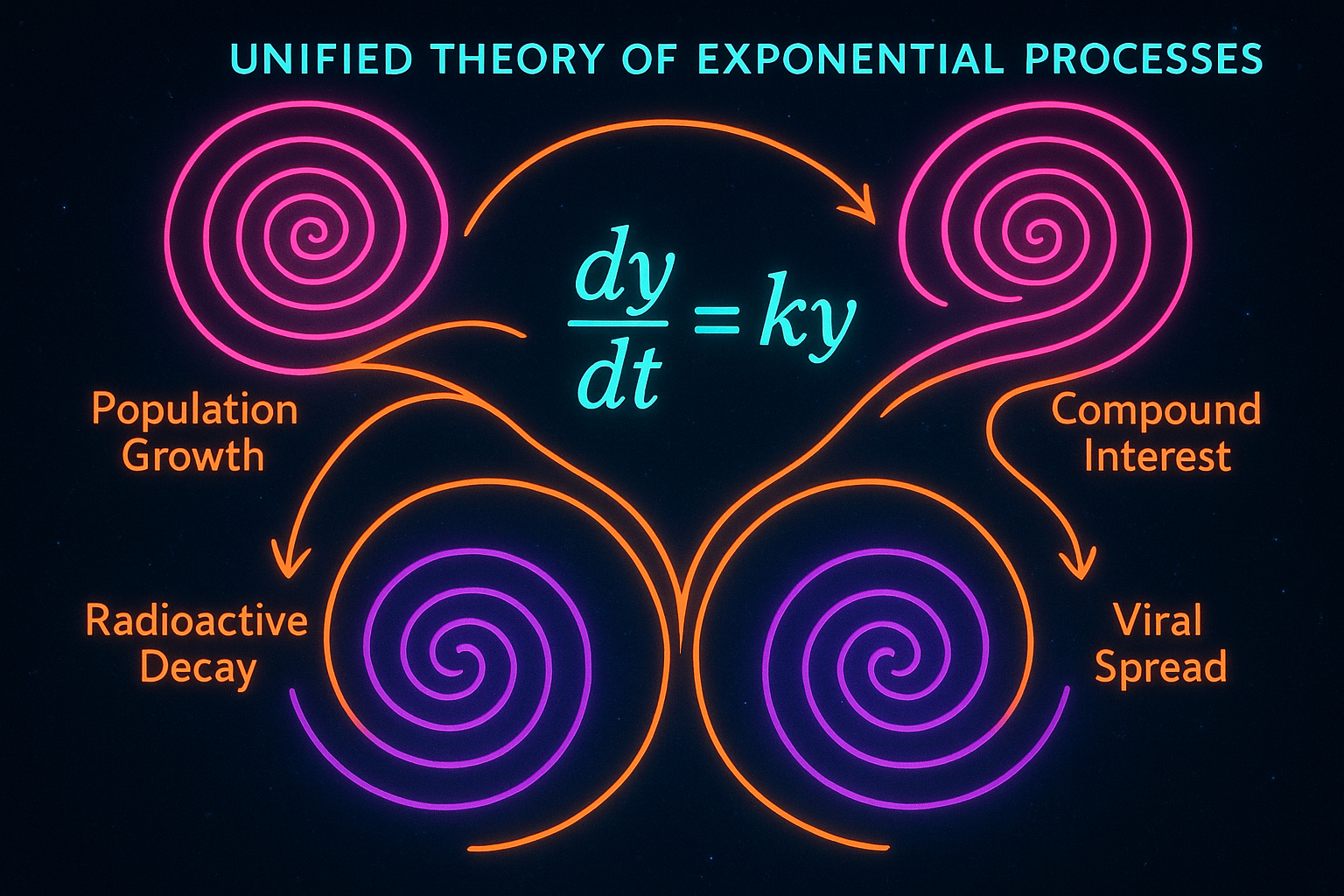
- Population growth — Bacteria double, humans multiply, viruses spread
- Financial growth — Compound interest, investments, debt
- Radioactive decay — Half-lives and carbon dating
- Epidemic spread — Viruses grow exponentially until they don't
- Moore's Law — Computing power doubles every ~2 years
Any process where the rate of change depends on the current amount is exponential. The bigger it gets, the faster it grows. The smaller it gets, the slower it shrinks.
Understanding exponential functions means understanding feedback loops, tipping points, and why "just a few more doublings" can change everything.
This is the hub page for the Exponential Functions series.
Next: What Is an Exponential Function? When the Variable Is the Power
The Series
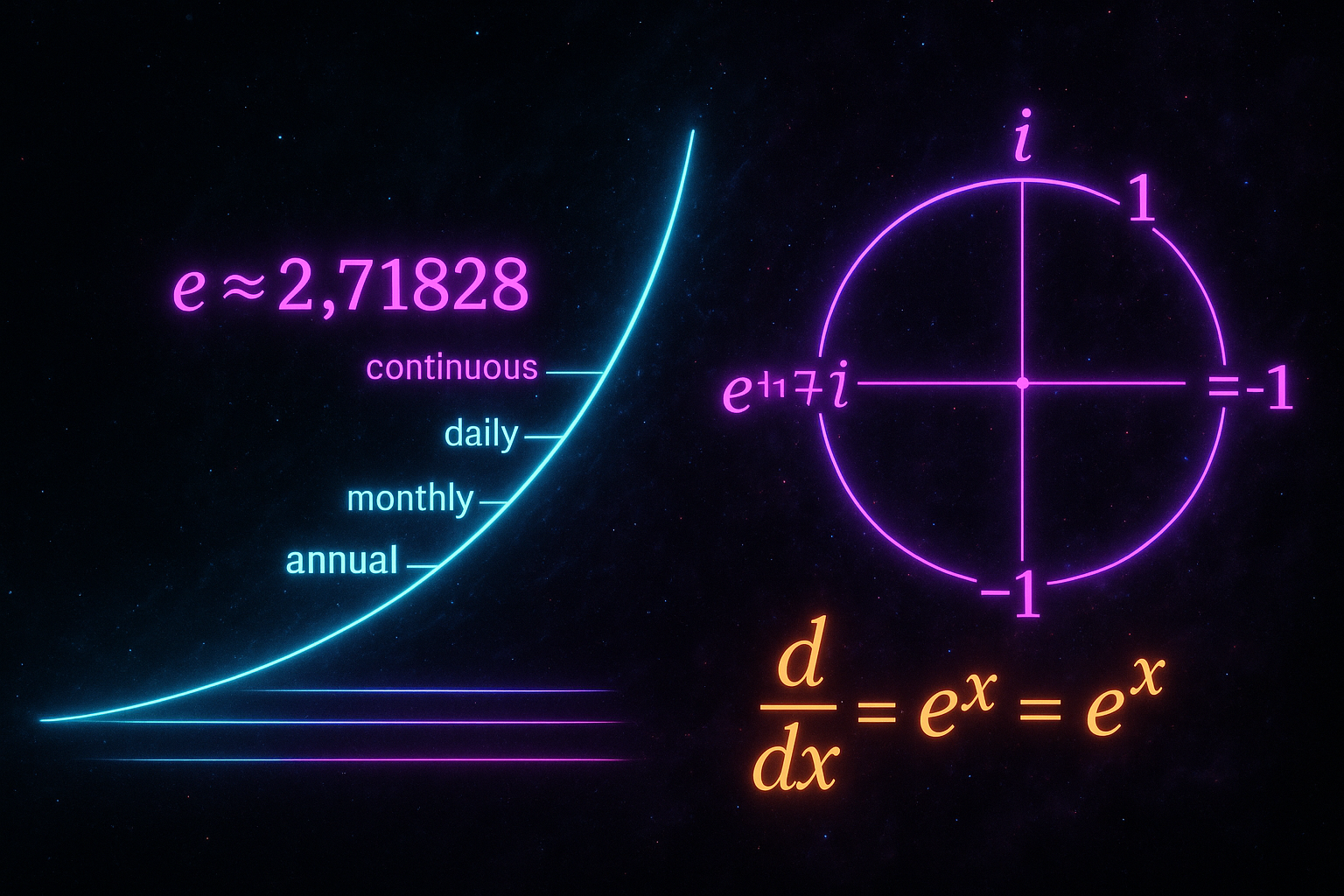
Comments ()