Linear Algebra Explained
Linear algebra isn't about algebra. It's about transformation.
Most of high school math teaches you to solve for x. Linear algebra teaches you to see space itself as something you can stretch, rotate, and shear. It's the mathematics of structure—how things change while preserving certain relationships.
Think of it this way: geometry shows you shapes. Calculus shows you change. Linear algebra shows you how change happens—the machinery of transformation itself.
What Linear Algebra Does
Every time your phone's screen rotates, linear algebra calculates the transformation. Every time Netflix recommends a show, linear algebra finds patterns in high-dimensional space. Every time a neural network recognizes your face, linear algebra transforms pixel data through layers of mathematical machinery.
This isn't abstract math hiding in textbooks. It's the operating system of the modern world.
Linear algebra gives you:
- Vectors — quantities with magnitude and direction
- Matrices — machines that transform vectors
- Transformations — operations that preserve structure
- Spaces — abstract arenas where addition and scaling work
Why It Matters
Linear algebra is the language of:
- Machine learning and AI
- Computer graphics and game engines
- Quantum mechanics
- Economics and optimization
- Signal processing
- Data compression
If you want to understand how modern technology actually works—not just use it, but understand it—you need linear algebra.
The Core Insight
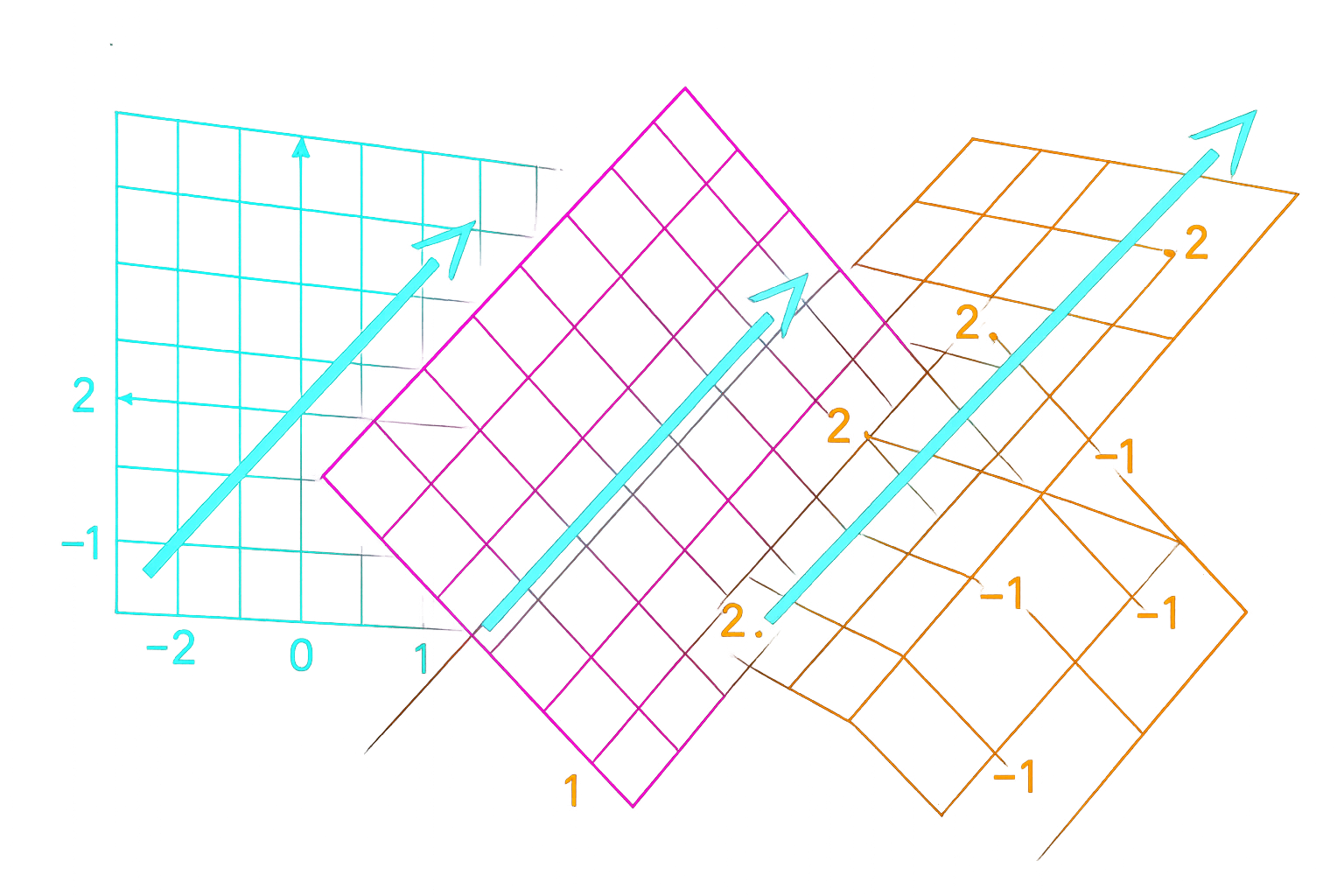
Here's the thing that makes linear algebra different from everything else you've learned: it's about preserving structure through change.
When you multiply a vector by a matrix, you're not just doing arithmetic. You're asking: What happens to this thing when space itself transforms?
That question—what survives transformation—turns out to be one of the most powerful ideas in mathematics. It connects geometry to algebra, physics to computation, abstract theory to concrete application.
What You'll Learn
This series will take you from vectors to vector spaces, from matrices to eigenvalues, from concrete calculations to abstract insights. We'll build intuition first, then formalism. We'll use examples you can visualize, then show you why the patterns generalize.
By the end, you'll see linear algebra not as a collection of procedures, but as a unified way of thinking about transformation, dimension, and structure.
You'll understand why matrices multiply the way they do. Why determinants measure volume. Why eigenvalues matter. Why basis vectors are coordinates in disguise.
You'll speak the language that underlies machine learning, quantum computing, and computer graphics. You'll see the mathematical structure that makes the modern world possible.
Linear algebra is the math of transformation. Let's learn how to transform.
This is the hub page for the Linear Algebra series.
Next: What Is Linear Algebra? The Mathematics of Many Dimensions
The Series



Comments ()